Technical
Difference ICW and SA protective plates
ICW = In Conjunction With = Must be combined with Level IIIA Soft Armor in order to achieve the declared protection level
SA = Stand Alone = Achieves the declared protection level without the use of additional soft armor.
First- & Second Focal Plane
FFP = First Focal Plane: The reticle values (subtensions) remain the same across the rifles’ magnification range.
SFP = Second Focal Plane: The reticle values (subtensions) are only valid at a certain magnification, usually at full magnification.
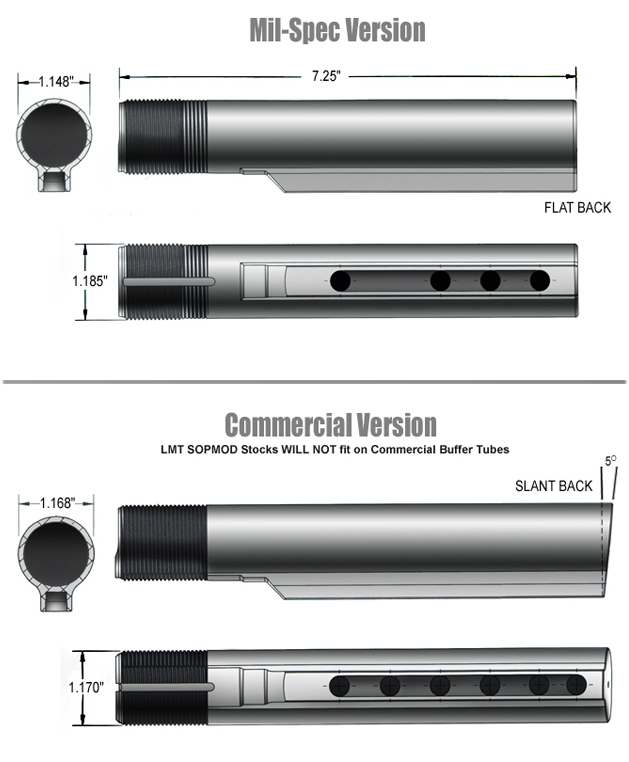
Mil-Spec versus Com-Spec AR15 Buffer Tube
Diameter Mil Spec: 1.148 Inch (= 2.916 cm)
Diameter Com Spec: 1.168 Inch (= 2.967 cm)
1 Inch = 2.54cm
NIJ Body Armor Classification Levels
Personal body armor covered by this standard is classified into five types (IIA, II, IIIA, III, IV) by level of ballistic performance. In addition, a special test class is defined to allow armor to be validated against threats that may not be covered by the five standard classes. The classification of an armor panel that provides two or more levels of NIJ ballistic protection at different locations on the ballistic panel shall be that of the minimum ballistic protection provided at any location on the panel.
2.1 Type IIA (9 mm; .40 S&W)
Type IIA armor that is new and unworn shall be tested with 9 mm Full Metal Jacketed Round Nose (FMJ RN) bullets with a specified mass of 8.0 g (124 gr) and a velocity of 373 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1225 ft/s ± 30 ft/s) and with .40 S&W Full Metal Jacketed (FMJ) bullets with a specified mass of 11.7 g (180 gr) and a velocity of 352 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1155 ft/s ± 30 ft/s). Type IIA armor that has been conditioned shall be tested with 9 mm FMJ RN bullets with a specified mass of 8.0 g (124 gr) and a velocity of 355 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1165 ft/s ± 30 ft/s) and with .40 S&W FMJ bullets with a specified mass of 11.7 g (180 gr) and a velocity of 325 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1065 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
2.2 Type II (9 mm; .357 Magnum)
Type II armor that is new and unworn shall be tested with 9 mm FMJ RN bullets with a specified mass of 8.0 g (124 gr) and a velocity of 398 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1305 ft/s ± 30 ft/s) and with .357 Magnum Jacketed Soft Point (JSP) bullets with a specified mass of 10.2 g (158 gr) and a velocity of 436 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1430 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
Type II armor that has been conditioned shall be tested with 9 mm FMJ RN bullets with a specified mass of 8.0 g (124 gr) and a velocity of 379 m/s ±9.1 m/s (1245 ft/s ± 30 ft/s) and with .357 Magnum JSP bullets with a specified mass of 10.2 g (158 gr) and a velocity of 408 m/s ±9.1 m/s (1340 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
2.3 Type IIIA (.357 SIG; .44 Magnum)
Type IIIA armor that is new and unworn shall be tested with .357 SIG FMJ Flat Nose (FN) bullets with a specified mass of 8.1 g (125 gr) and a velocity of 448 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1470 ft/s ± 30 ft/s) and with .44 Magnum Semi Jacketed Hollow Point (SJHP) bullets with a specified mass of 15.6 g (240 gr) and a velocity of 436 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1430 ft/s ± 30 ft/s). Type IIIA armor that has been conditioned shall be tested with .357 SIG FMJ FN bullets with a specified mass of 8.1 g (125 gr) and a velocity of 430 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1410 ft/s ± 30 ft/s) and with .44 Magnum SJHP bullets with a specified mass of 15.6 g (240 gr) and a velocity of 408 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (1340 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
2.4 Type III (Rifles)
Type III hard armor or plate inserts shall be tested in a conditioned state with 7.62 mm FMJ, steel jacketed bullets (U.S. Military designation M80) with a specified mass of 9.6 g (147 gr) and a velocity of 847 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (2780 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
Type III flexible armor shall be tested in both the “as new” state and the conditioned state with 7.62 mm FMJ, steel jacketed bullets (U.S. Military designation M80) with a specified mass of 9.6 g (147 gr) and a velocity of 847 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (2780 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
For a Type III hard armor or plate insert that will be tested as an in conjunction design, the flexible armor shall be tested in accordance with this standard and found compliant as a stand-alone armor at its specified threat level. The combination of the flexible armor and hard armor/plate shall then be tested as a system and found to provide protection at the system’s specified threat level. NIJ-approved hard armors and plate inserts must be clearly labeled as providing ballistic protection only when worn in conjunction with the NIJ-approved flexible armor system with which they were tested.
2.5 Type IV (Armor Piercing Rifle)
Type IV hard armor or plate inserts shall be tested in a conditioned state with .30 caliber armor piercing (AP) bullets (U.S. Military designation M2 AP) with a specified mass of 10.8 g (166 gr) and a velocity of 878 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (2880 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
Type IV flexible armor shall be tested in both the “as new” state and the conditioned state with .30 caliber AP bullets (U.S. Military designation M2 AP) with a specified mass of 10.8 g (166 gr) and a velocity of 878 m/s ± 9.1 m/s (2880 ft/s ± 30 ft/s).
For a Type IV hard armor or plate insert that will be tested as an in conjunction design, the flexible armor shall be tested in accordance with this standard and found compliant as a stand-alone armor at its specified threat level. The combination of the flexible armor and hard armor/plate shall then be tested as a system and found to provide protection at the system’s specified threat level. NIJ-approved hard armors and plate inserts must be clearly labeled as providing ballistic protection only when worn in conjunction with the NIJ-approved flexible armor system with which they were tested.
What is an NSN?
A National Stock Number (NSN), as it is known in the US, or a NATO Stock Number, is a 13-digit numeric code identifying all the “standardized material items of supply” as they have been recognized by all NATO countries including the US Department of Defense. An item having an NSN is said to be “stock-listed,” which expedites the purchase process for military or government customers.
Protection standards for spectacles & goggles
ANSI Z87.1
ANSI is the American National Standard that covers the basic requirements for personal eye as well as face protection to minimize e.g. accidents from impacts.
EN ISO 12312-1
EN ISO 12312-1:2013 is the European Standard that specifies the special requirements (mechanical, optical, and so on) for sunglasses and sunglare filters for protection against solar radiation for general use etc.
EN 166
The eye protection regarding the professional life is regulated with the norm EN166. It is the standard European norm for the personal eye protection specifications which classified the eye protection in detail.
MIL-PRF-31013
MIL-PRF-31013 is a US military standard for open spectacles and special performance protective eyewear to test its ballistic effectiveness.
MIL-DTL-43511D
MIL-DTL-43511D is a US military standard for closed goggles and special performance protective eyewear to test its ballistic effectiveness.
STANAG 2920/4296
The NATO abbreviation STANAG stands for Standardization Agreement which sets up conditions, terms, technical procedures etc. between the alliance members. This test, which is called V-50, is the adaption of standards for ballistic protection levels / testing of a glass that is shot with a special buckshot. The measured value is the arithmetic mean of the set of measured velocities.
Why is the front lens of my red dot sight at an angle?
Red Dot Lens Positioning: All red dot sights have an objective lens at the front of the unit that is spherical in shape. However, unlike a conventional riflescope, the objective lens in a red dot sight is positioned off axis and appears to be tilted when looking at the sight. This angle of the front lens allows the light generated by the battery powered LED light source inside the unit to be reflected back into the sight. The reflected light becomes the "dot" or aiming reference that the user sees when a red dot sight is switched on.
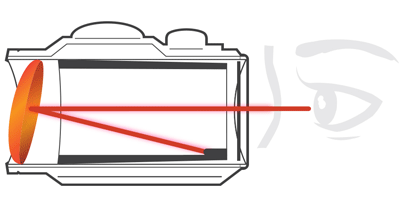
This engineered "bending" of light is what makes today's red-dot sights so popular and easy to use. Adhesive is used on the inside of the sight to secure the LED to the inside of the tube. By design, the led package intrudes slightly on the field of view.










